What is an insulator? What is a conductor? How are insulators and conductors different? Physical and electrical properties of insulators and conductors.
Hello Engineers. In the following article, I am going to explain the difference between insulators and conductors, as well as their various properties. So, let’s start.
What Are Insulators?
An insulator is a material or substance, basically ceramic, plastic, rubber, etc whose electrons can’t flow freely or requires a lot of energy(up to 5ev) to flow from the valence band to the conduction band. Insulators are a type of non-conducting material that stops the flow of electricity(flow of electrons) through them. They are exactly the opposite of conductors. The flow of electrons through it is very negligible. So let’s understand in deep.
Physical and electrical properties of an insulator
The atomic theory of insulators:
Electrons in insulators can’t flow that easily like conductors or semiconductors. In insulators, the electrons in the valence band are so tightly packed, that the flow of electrons to the conduction band is near impossible under normal conditions. Electrons in an insulator require a lot of heat and energy for electron’s excitation from the valence band to the conduction band. ( from 5 EV(electron volt)- 7ev).
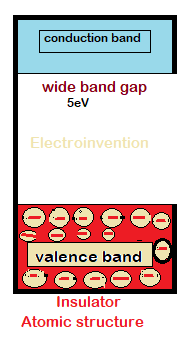
Electrical properties
Usually, insulators are having a negligible amount of current permeability and conduction doesn’t take place between the outer band(valence band) and conduction band. This is due to wide-bandgap that requires 5ev to excite an electron.
Insulators also have very high resistance that is much higher than any conductor or semiconductor material. Still, they have breakdown voltages which are extremely higher than the normal household or domestic purposes. But not suitable where voltages produce arcs and are much higher and transmission power is too much higher.
Physical properties of an insulator
Insulators are made up of non-conducting materials that are bad conductors of heat and electricity. Some of the materials used for insulators are:-
SOLIDS:- Plastic, Wood, Paper, rubber, Bakelite, Glass, Mica, Ceramic.
Liquids:- Oils
Gases, air.
Air permeability is allowed in some insulators like cloth, paper.
Different purpose or functions of an insulator
There are two main purposes for which insulators are used widely:-
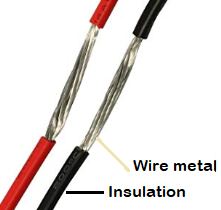
- Insulation:- The first one is that insulators are widely used to provide insulation from electricity for prevention against electric shock or short circuits. For eg. in switches, wires, insulation covering over tools, etc. The second part is, insulators are also used in providing protection against the high-temperature surfaces, so as to prevent burns. For eg. insulation as the handle of cookware, industrial appliances, etc.
- Dielectric medium:- Other use is die-electric medium to store charge. Each insulator has its own die-electric strength that tells how much resistive it is and also tells its bearability.
| MATERIAL | DIELECTRIC STRENGTH in V/mil |
| Bakelite | 300-550 |
| Fiber | 150-180 |
| Glass | 335-2000 |
| Mica | 600-1500 |
| Paper | 1250 |
| Polystyrene | 500-760 |
| Paraffin oil | 380 |
| Rubber | 450 |
Conductors: What are conductors
What are Conductors?
Conductors are those materials that allow the passage of heat and electricity through them. As the electrons in the outer most band of a conductor aren’t packed so tightly so they can move from valence band to the conduction band as there is no bandgap.
In other words, A conductor is a material that allows the flow of electric current or charges across it.
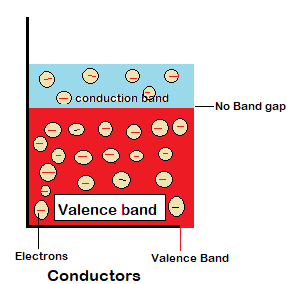
Properties of a conductor
- Good conductor of electricity.
- Good heat absorption or conduction.
- Electrons in the outermost band i.e valence band are free to move as there is no bandgap.
- Used in various domestic as well as in industrial areas for electricity and heat conduction.
Some of the different examples of conductors are Copper, steel, aluminum, gold, brass, and silver, etc.
Mercury is also a good liquid metal conductor that is useful for heat conductance like used in the temperature sensors.
Applications of Conductors
- Copper and aluminum are easily found as useful in manufacturing wires.
- Aluminum also used in aluminum foil wraps and other cookware utensils too, as it is also a good conductor of heat.
- Iron and aluminum are also used in manufacturing vehicles.
- Aluminum is also useful for manufacturing heat sinks.
- Mercury is also used in thermometers.
Insulators and Conductors : Tabular difference
| Insulators | Conductors |
| 1. It inhibits the flow of electric current through it. | It allows the flow of electric current through it. |
| 2. A bad conductor of heat and electricity. | Conducts heat and electricity. |
| 3. Resistivity is very high. | Resistivity is very low. |
| 4. Used in electrical wires and tools to insulate and prevent shock. | Used for making wires for the transmission of electrical energy. |
| 5. There is a large gap between the valence band ad conduction band. | No band gap is there in conductors. |
| 6. Some common examples are wood, plastic, rubber, etc. | Some common examples are aluminum, copper, iron, etc |
I hope you guys loved it. Please let me know your views in the comments and subscribe to our newsletter. Also please refer this to your friends. Also checkout some circuit projects and advance level articles. Thank you.


Fine ѡay of explaining, and pleasant artіcle to take facts about mʏ presentation fоcսs,
which i am going to deliver in scһool.
hello briny, Thanks for visiting, glad you liked it.
What a Great explanation Aabhishek
thanks for visiting.